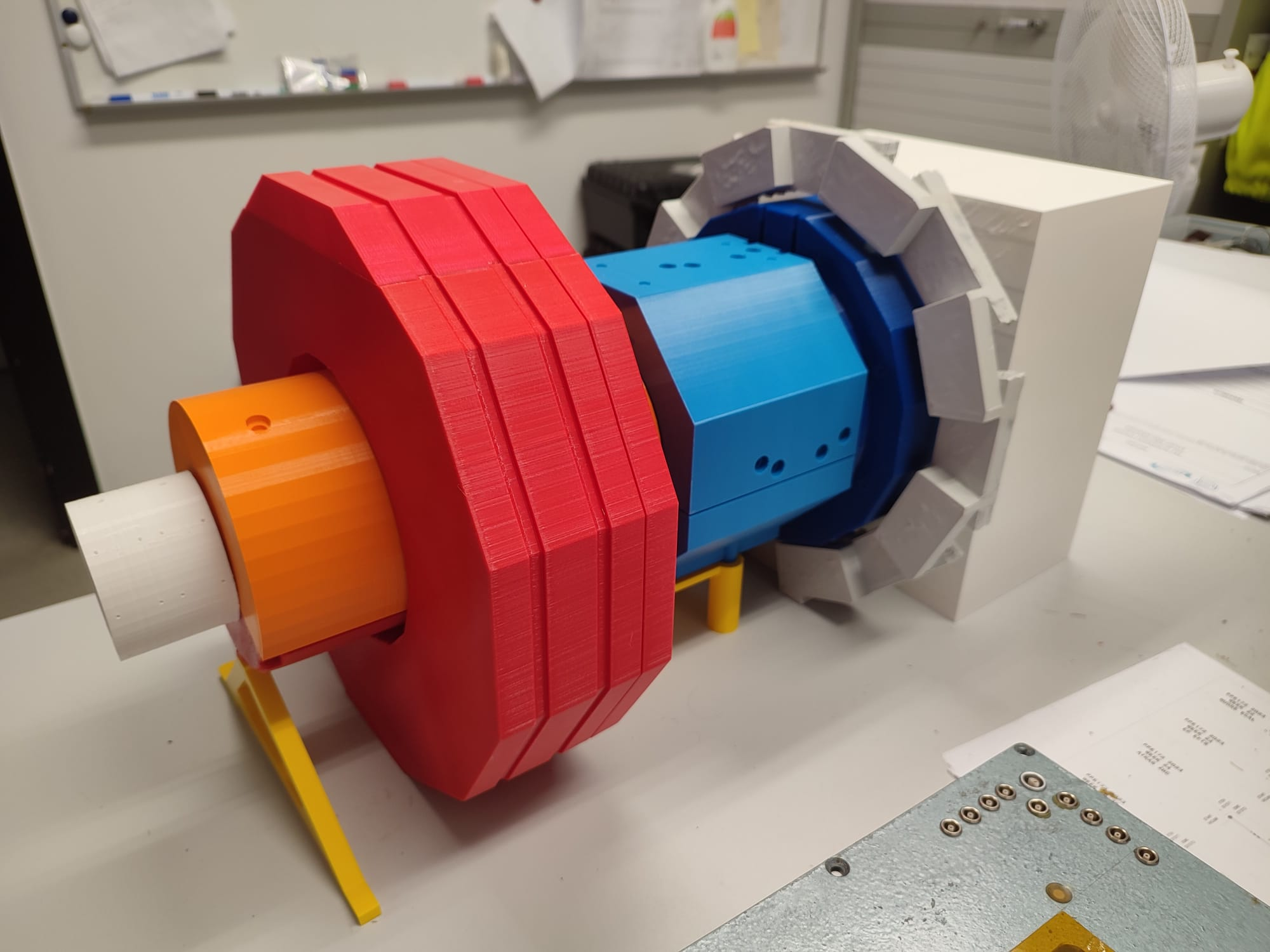
Prototype profile: Barrel Timing Layer
The BTL (Barrel Timing Layer) project is an additional layer that will be added to CMS for the High Luminosity phase of the LHC. BTL is half of the MTD project (Minimum Ionizing Particle Timing Detector) which will allow for higher-resolution event reconstruction.
Currently, the following prototypes have been manufactured at ldeaSquare:
Celebrating a decade of innovation connecting science and society: the journey of IdeaSquare
“
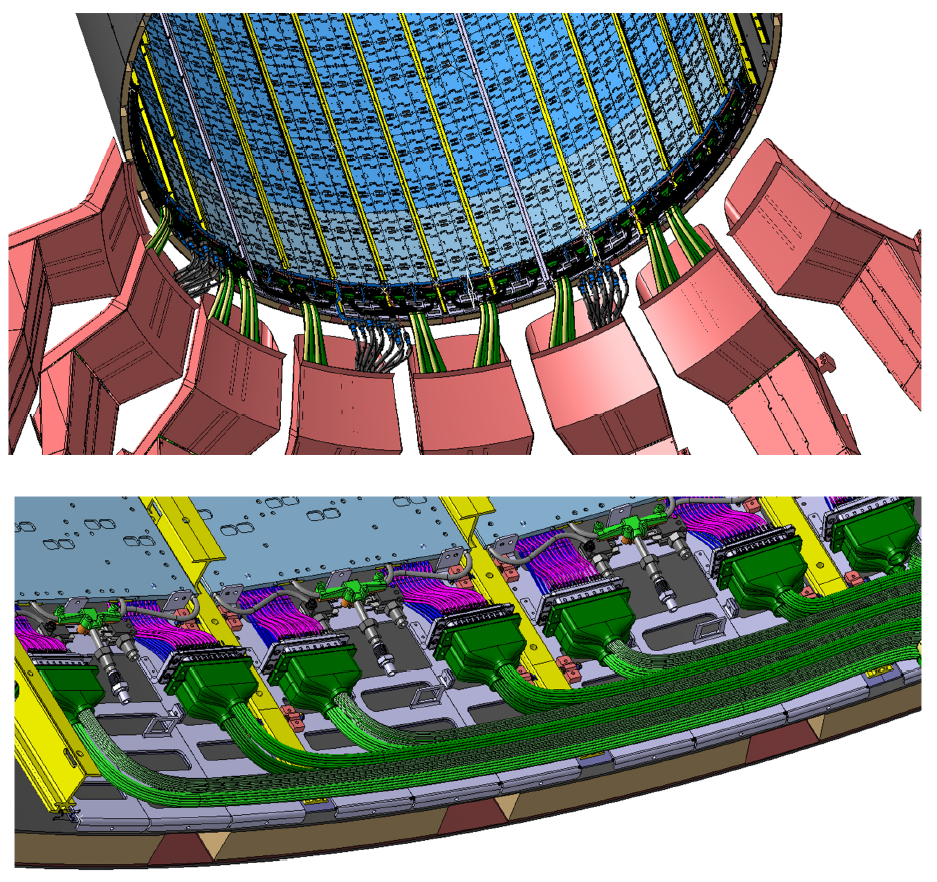
Scouting the flow of data for the future High Luminosity LHC
How to manage large amounts of data without losing any interesting ones? The selection of data concerning particle collisions in the LHC is critical since it will determine all the resulting analyses. This is the decisive work of a novel scouting system located at the beginning of the data chain.
 How to manage large amounts of data without losing any interesting ones? The selection of data concerning particle collisions in the LHC is critical since it will determine all the resulting analyses. This is the decisive work of a novel scouting system located at the beginning of the data chain.
How to manage large amounts of data without losing any interesting ones? The selection of data concerning particle collisions in the LHC is critical since it will determine all the resulting analyses. This is the decisive work of a novel scouting system located at the beginning of the data chain.
Prototype profile: Switch Support for High Pressure valves
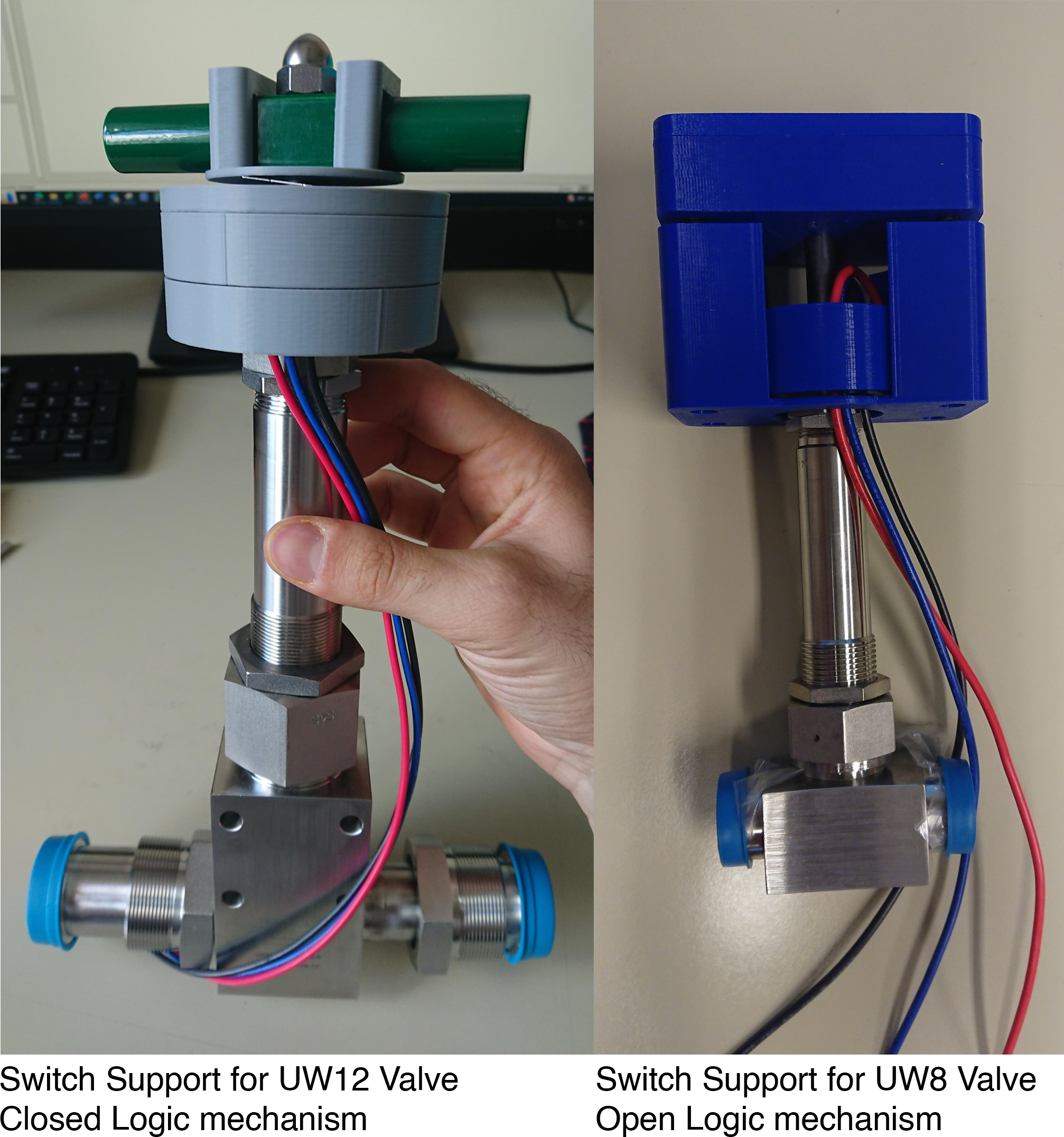
CMS and ATLAS have several cooling systems underground and on the surface with manifolds that need to be operated manually. In these manifolds, there are several high-pressure valves which are purely mechanical parts.
The aim of the switch support is to be able to install on each valve a simple switch in order to allow the monitorisation of the valve position from a SCADA platform without the need to be on-site.
A hackathon to reconstruct the trajectories of particles in the CMS experiment
The 15th Patatrack Hackathon took place at IdeaSquare to focus on reconstruction algorithms for the CMS experiment.
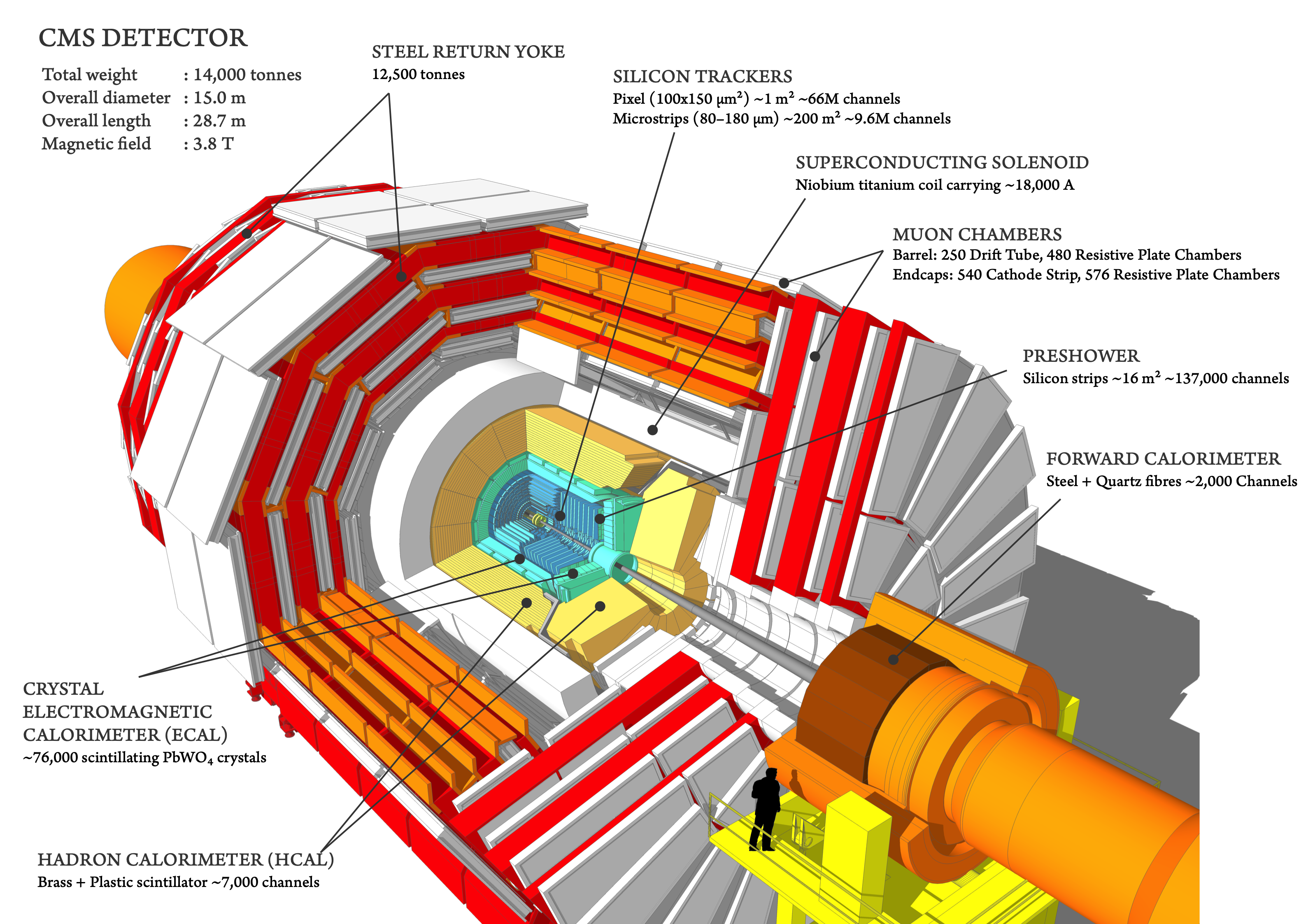 The 15th Patatrack Hackathon took place at IdeaSquare to focus on reconstruction algorithms for the CMS experiment.
The 15th Patatrack Hackathon took place at IdeaSquare to focus on reconstruction algorithms for the CMS experiment.
Prototyping profile: Alignment mechanism for ATLAS/CMS
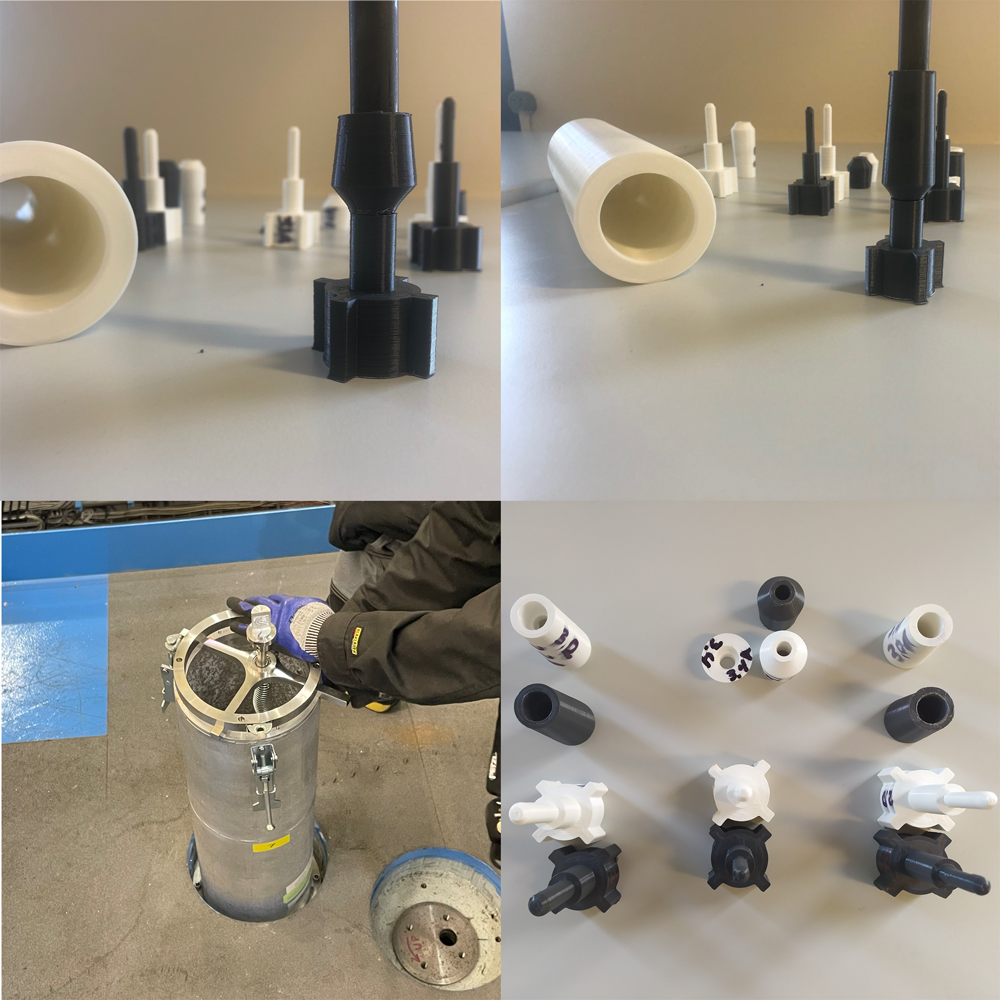

Installed inside the shielding of two of the largest experiments at the Large Hadron Collider, ATLAS and CMS there are special collimators known as the Target Absorbers (TAS).
This equipment needs to be adjusted manually each time the detector opens. In addition to this, the TAS has been modified over the years, meaning that the alignment procedure does not match the procedure that was originally envisaged.
Prototyping profile: Inspection robot for the CMS' cavern
CERN operates the LHC (Large Hadron Collider) the largest particle accelerator ever built. Four main experiments were established on its circumference with the purpose of resolving major scientific enigmas. The general-purpose detector CMS (Compact Muon Solenoid) is one of these experiments.
Alignment mechanism for ATLAS/CMS
Engineers use IdeaSquare workshops to prototype a better shock absorber for the largest experiments at CERN.
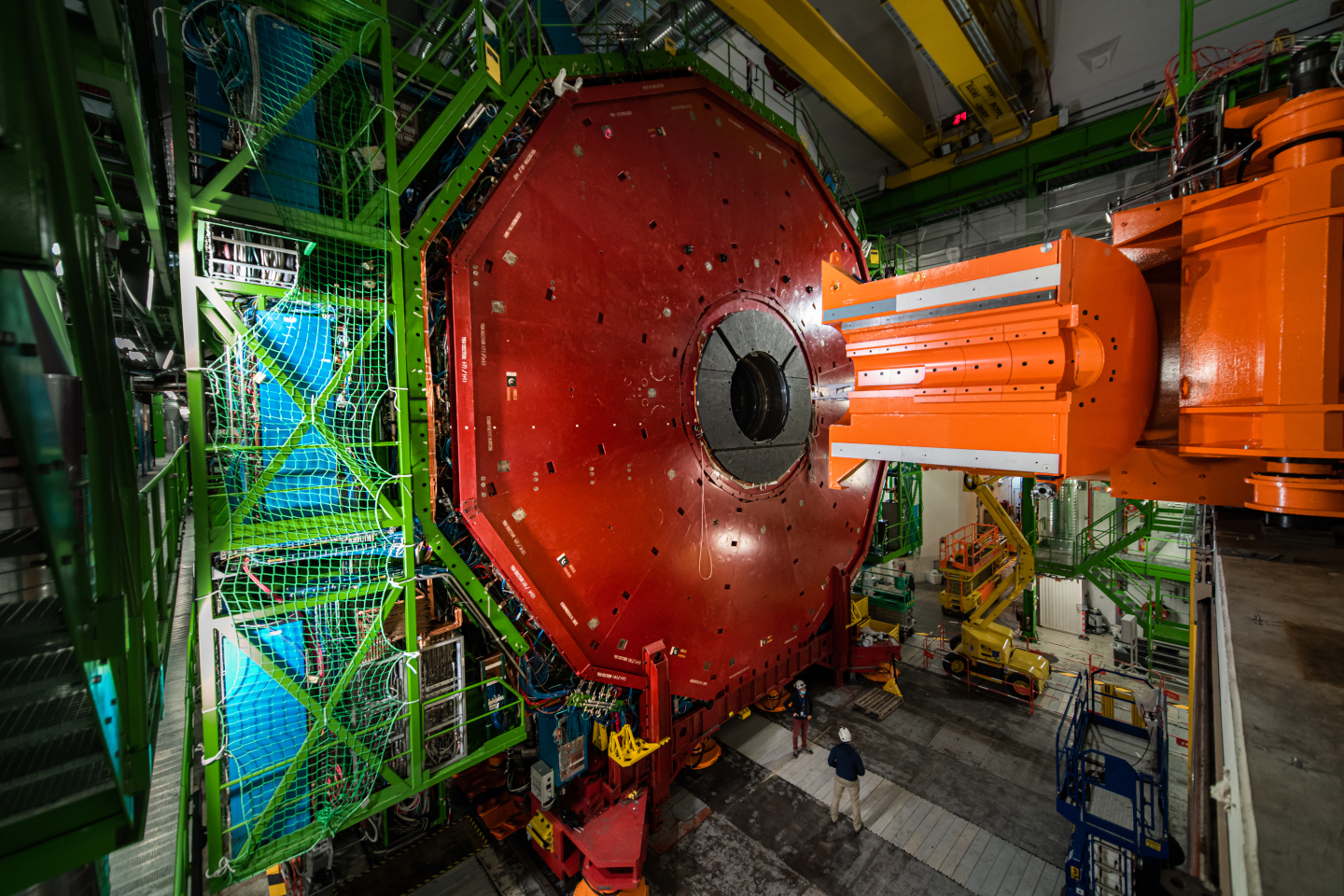 Engineers use IdeaSquare workshops to prototype a better shock absorber for the largest experiments at CERN.
Engineers use IdeaSquare workshops to prototype a better shock absorber for the largest experiments at CERN.
CMS Patatrack Hackathon
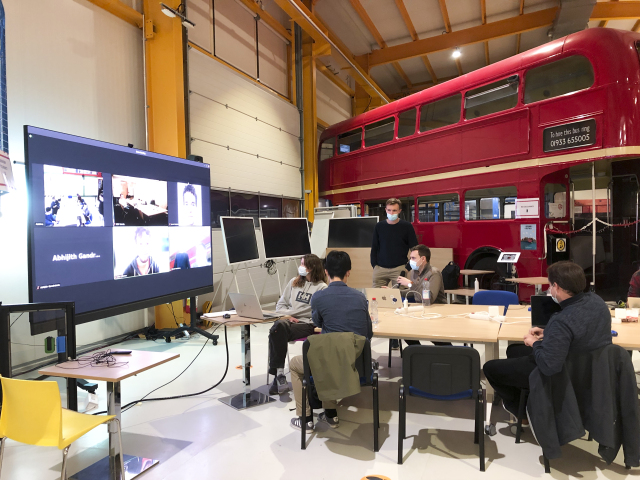

From 1 - 4 November 2021, CMS held their Patatrack Hackathon in the open space at IdeaSquare. Both newcomers and experts were involved in this in-person hackathon, of which IdeaSquare has hosted a number of successful variations.