New system for booking our prototyping workshops
Everyone from the CERN community - researchers, EU project collaborators, students and guests - is welcome to take advantage of our space to put innovative ideas to the test.
Over 200 CERN personnel use IdeaSquare’s space every year. With easily accessible 3D printers, laser cutters, and interactive smartboards, CERN users can quickly build and experiment with prototypes. Use of our facilities is free of charge, unless larger volumes of materials are required.
Prototype exhibition opens at IdeaSquare
What if our student projects could unlock unseen solutions for global challenges?
 What if our student projects could unlock unseen solutions for global challenges?
What if our student projects could unlock unseen solutions for global challenges?
ATTRACT celebrates successes at final conference
The initiative helped develop breakthrough detection and imaging technologies and tested a model for innovation in Europe
 The initiative helped develop breakthrough detection and imaging technologies and tested a model for innovation in Europe
The initiative helped develop breakthrough detection and imaging technologies and tested a model for innovation in Europe
Prototype profile: Barrel Timing Layer
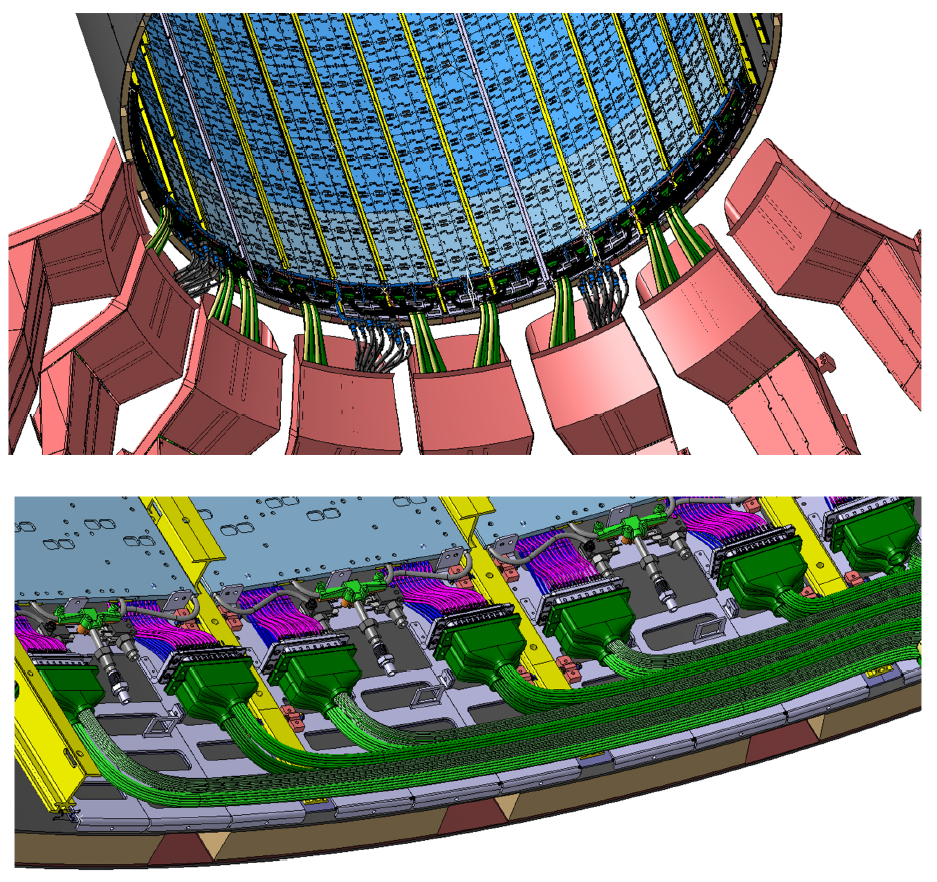
The BTL (Barrel Timing Layer) project is an additional layer that will be added to CMS for the High Luminosity phase of the LHC. BTL is half of the MTD project (Minimum Ionizing Particle Timing Detector) which will allow for higher-resolution event reconstruction.
Currently, the following prototypes have been manufactured at ldeaSquare:
Prototype profile: FASERCal detector
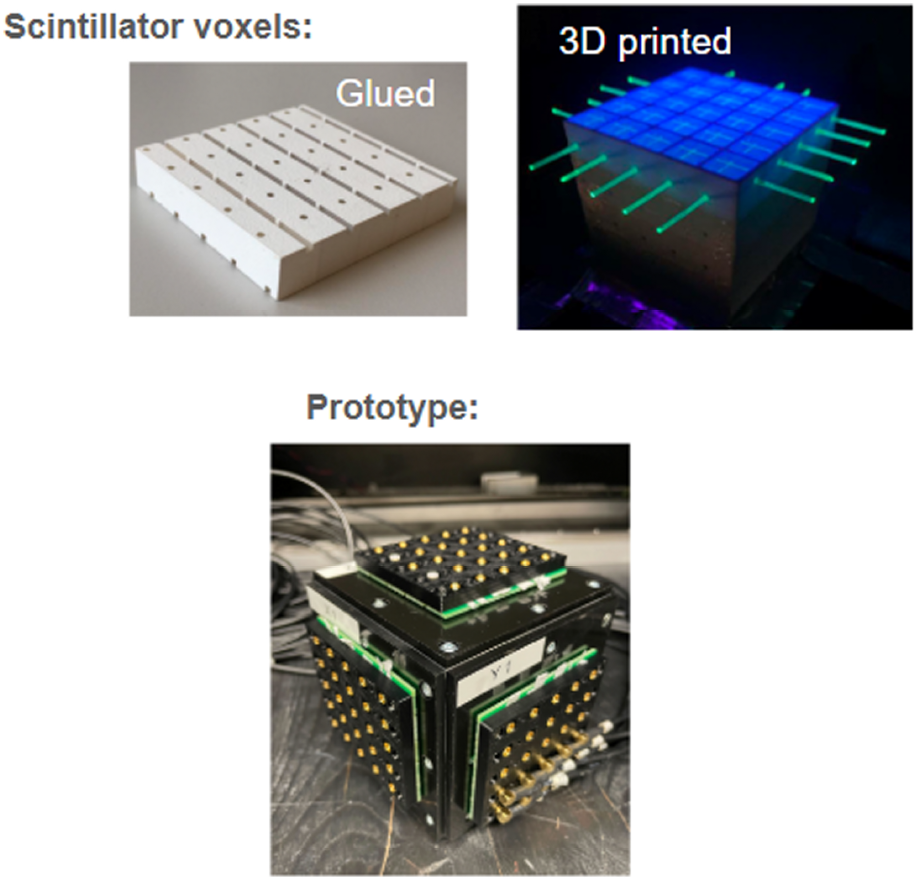
A proposed detector to be placed next to the FASER experiment in the LHC. The main component of FASERCal is the "3DCal" that will allow 3D track reconstruction of particles. Current prototypes are being developed at ETH for these 3DCal modules.
- Optically isolated 1 cm3 cubes, readout fibres
- arranged in three planes to collect light from multiple cubes
- 3D voxel reconstruction
Prototype profile: Stirling cryo-cooler
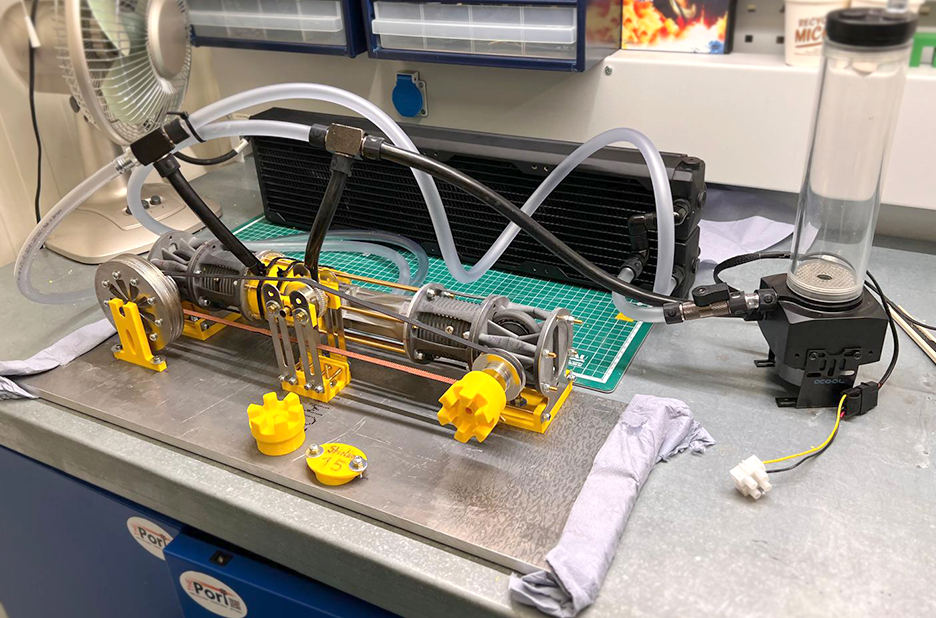
A Stirling machine is a device, that can be used as a heat pump to effectively cool down a given system. In reverse it can be used to generate electricity out of a heat source. It was invented 200 years ago and has not been improved/changed greatly since then, as there was never an economic interest.
A workshop to introduce children from the Jardin des Particules to prototyping and teamwork
For three mornings, around forty children from the Jardin des Particules came to IdeaSquare, the innovation space at CERN, for an extraordinary workshop!
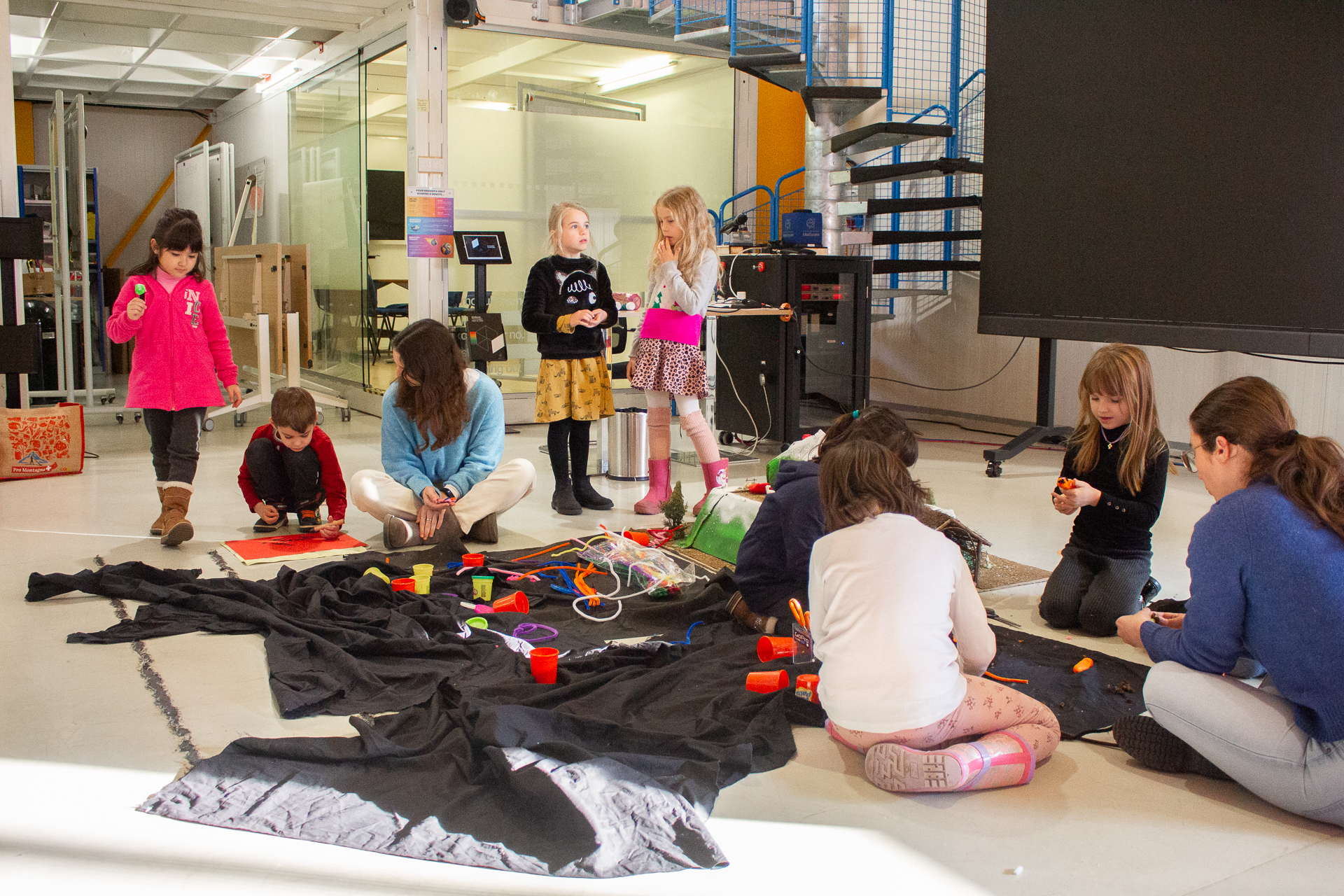 For three mornings, around forty children from the Jardin des Particules came to IdeaSquare, the innovation space at CERN, for an extraordinary workshop!
For three mornings, around forty children from the Jardin des Particules came to IdeaSquare, the innovation space at CERN, for an extraordinary workshop!
IdeaSquare as a shortcut between conceptualising and prototyping
Both working on the LHCb calorimeter, Matteo Salomoni and Kacper Jama used IdeaSquare extensively to develop new calorimeter modules that will be installed during the long shutdown 3. In this letter, they explain how crucial it was for them to be able to come and prototype at IdeaSquare for their project.
 Both working on the LHCb calorimeter, Matteo Salomoni and Kacper Jama used IdeaSquare extensively to develop new calorimeter modules that will be installed during the long shutdown 3. In this letter, they explain how crucial it was for them to be able to come and prototype at IdeaSquare for their project.
Both working on the LHCb calorimeter, Matteo Salomoni and Kacper Jama used IdeaSquare extensively to develop new calorimeter modules that will be installed during the long shutdown 3. In this letter, they explain how crucial it was for them to be able to come and prototype at IdeaSquare for their project.
How can I use CERN IdeaSquare?
Workshops and hackathons, prototyping facilities, events and more: find out how the CERN community can benefit from IdeaSquare, the innovation space at CERN
 Workshops and hackathons, prototyping facilities, events and more: find out how the CERN community can benefit from IdeaSquare, the innovation space at CERN
Workshops and hackathons, prototyping facilities, events and more: find out how the CERN community can benefit from IdeaSquare, the innovation space at CERN
Prototype profile: The South African Consortium of Air Quality Monitoring (SACAQM) AI_r system - solving the affordability problem with AI-powered IoT
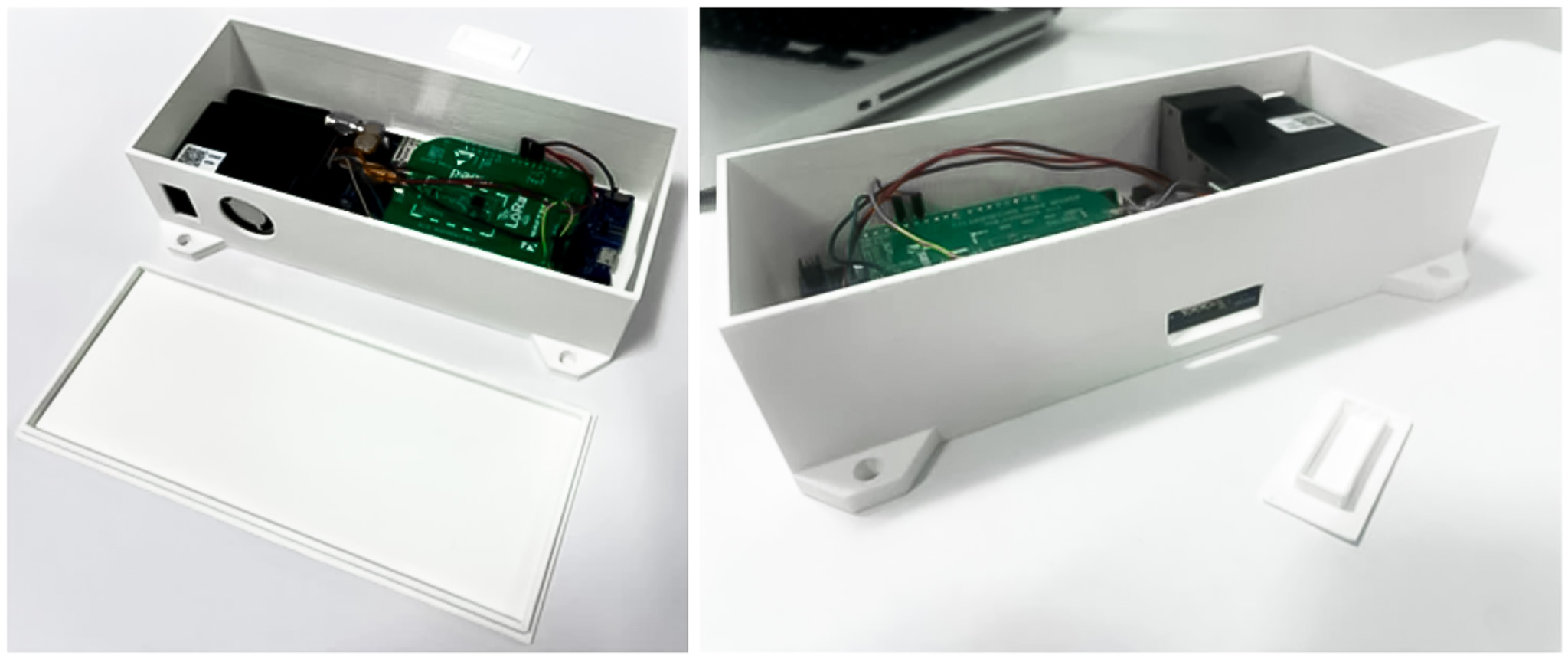
The SACAQM Al_r system is an air quality monitoring, analysis and prediction system. It leverages cutting-edge air quality sensors, an efficient loT network infrastructure, and advanced artificial intelligence to create a scalable, cost-effective solution.
This technology not only captures real-time air quality data but also employs Al to forecast future air quality conditions. By integrating state-of-the-art sensors with loT and Al capabilities, the Intelligent loT Air Quality Monitoring and Prediction System is positioned to address the limitations of existing systems.
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page