Scouting the flow of data for the future High Luminosity LHC
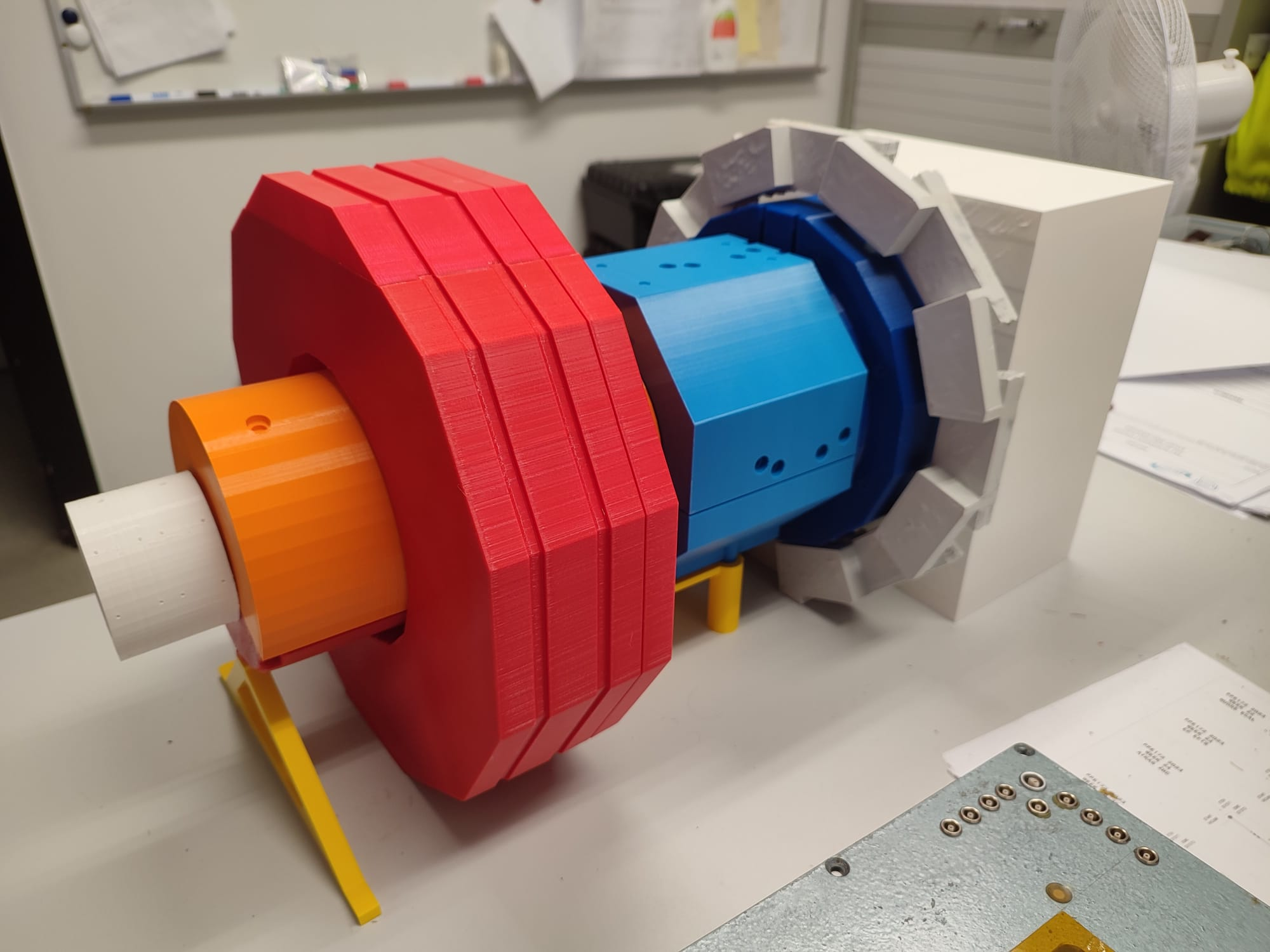
How to manage large amounts of data without losing any interesting ones? The selection of data concerning particle collisions in the LHC is critical since it will determine all the resulting analyses. This is the decisive work of a novel scouting system located at the beginning of the data chain.
 How to manage large amounts of data without losing any interesting ones? The selection of data concerning particle collisions in the LHC is critical since it will determine all the resulting analyses. This is the decisive work of a novel scouting system located at the beginning of the data chain.
How to manage large amounts of data without losing any interesting ones? The selection of data concerning particle collisions in the LHC is critical since it will determine all the resulting analyses. This is the decisive work of a novel scouting system located at the beginning of the data chain.
Prototype profile: LHC Vlead Tester Box
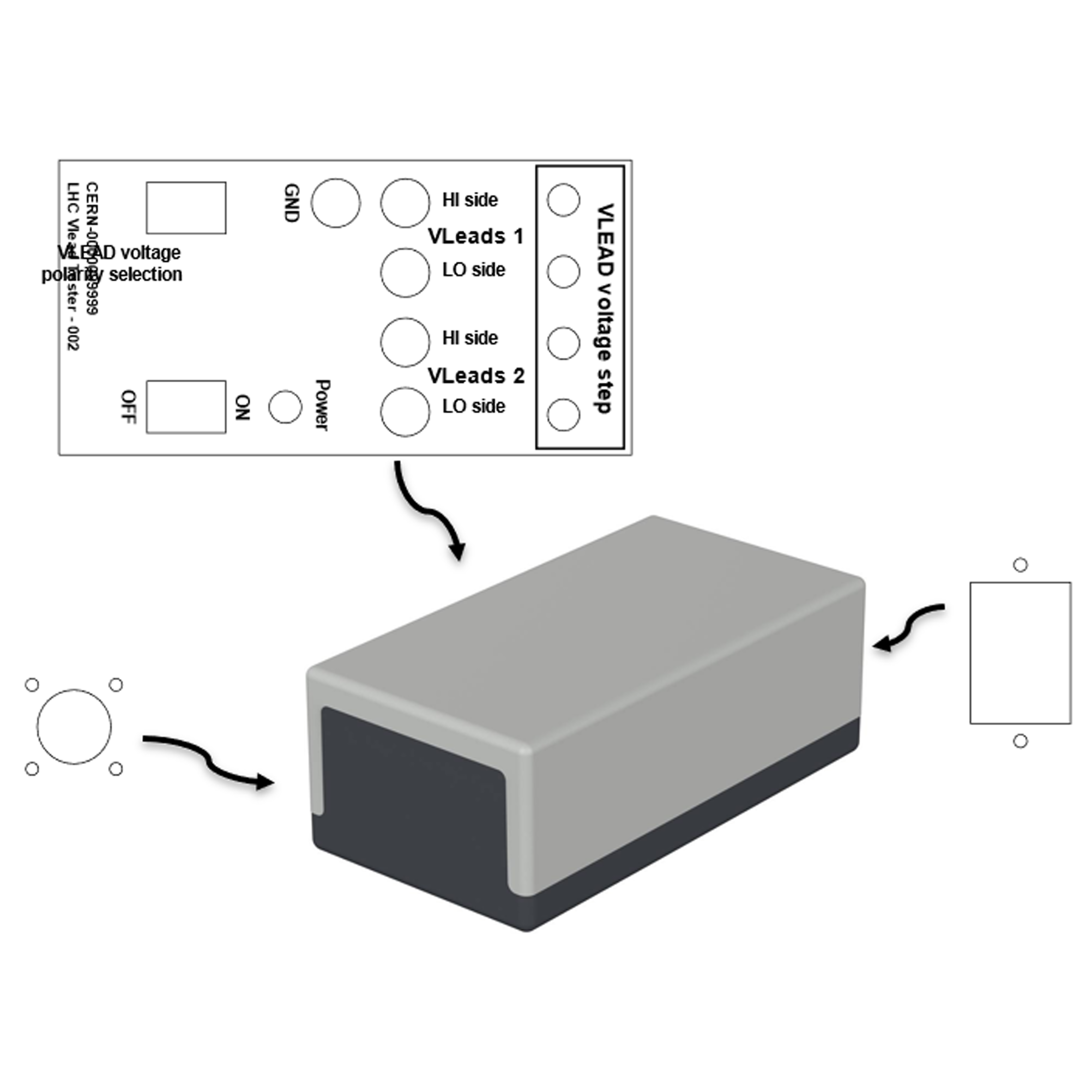
The box, called "LHC Vlead Tester", will be used to test power converters which supply current to superconducting magnets.
Because superconducting magnets are cooled to cryogenic temperatures there is a device called "current lead" that enables the connection of room-temperature conductors to cryogenic conductors. These current leads are critical devices, therefore the voltage across them is monitored by the power converter which will shut down if a certain voltage threshold is reached.
Prototype profile: Design and validation of a safe mechatronic system for the handling of radioactive sources

The LHC tunnel is a highly radioactive environment during the operation of the machine.
Four thousand Beam Loss Monitors (BLMs) are placed along the magnets to ensure no radiation escape. It is essential to verify the proper operation of each of these BLMs before operation to ensure safety.
Prototyping profile: Inspection robot for the CMS' cavern
CERN operates the LHC (Large Hadron Collider) the largest particle accelerator ever built. Four main experiments were established on its circumference with the purpose of resolving major scientific enigmas. The general-purpose detector CMS (Compact Muon Solenoid) is one of these experiments.